Mobile:023-67162778
Phone:18184765876
Fax:023-67162779
Email:kaperior@qq.com
Address:No. 88, Qinye Road, Konggang Industrial Park, Yubei District, Chongqing
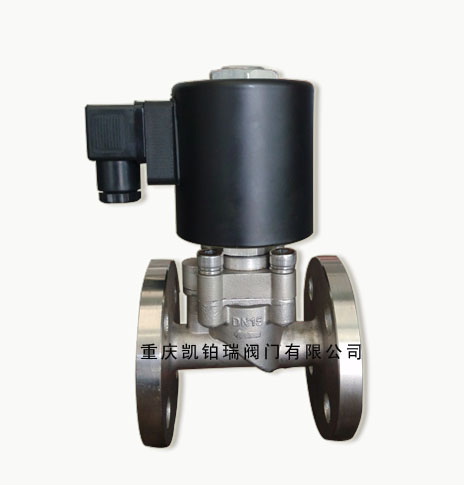

Overview of Bidirectional Solenoid Valve
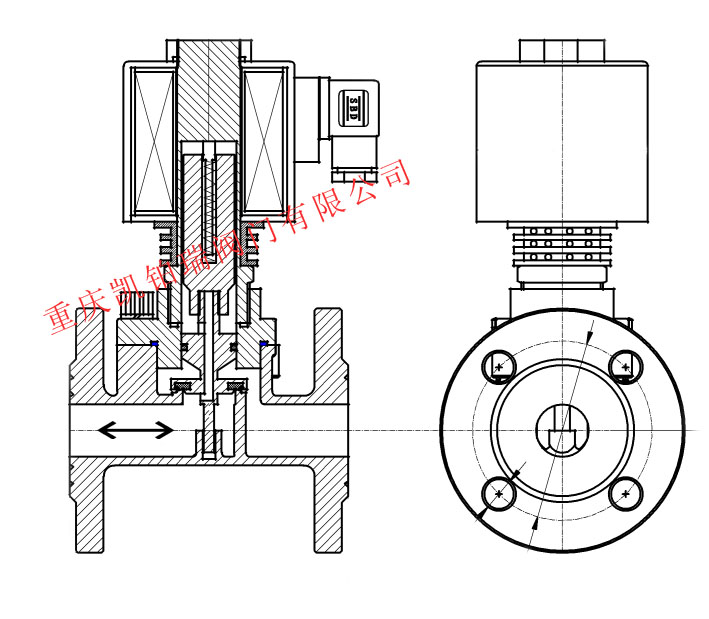
A bidirectional solenoid valve is a special working environment used in the same pipeline, where the inlet can flow to the outlet and the outlet can flow to the inlet, and whether it flows from the inlet to the outlet or from the outlet to the inlet, it can be completely enclosed. Our company has introduced German Parker solenoid valve technology and combined it with the zero leakage advantage of our own stainless steel flying disc piston to successfully develop a bidirectional solenoid valve. This bidirectional solenoid valve adopts a piston structure, which can adapt well to low and medium pressure environments. The successful development of this valve has also filled the gap in the Chinese two-way solenoid valve market.
1、 Characteristics of bidirectional solenoid valve
1. The valve is sealed with a stainless steel piston, completely preventing leakage;
2. Within the pressure range of use, the valve does not distinguish between inlet and outlet, meaning that both inlet and outlet can be used normally;
3. The coil adopts a special high-power coil to ensure the rapid opening and closing of the bidirectional solenoid valve;
4. Internally, special processed 304 stainless steel springs are used to ensure complete closure of the medium flow from the outlet to the inlet;
5. This valve can adopt a direct acting structure to meet the working conditions with very low operating pressure.
2、 Technical parameters of bidirectional solenoid valve
Caliber: DN10-DN500
Power supply voltage: DC6V-DC220V, AC12V-AC220V
Coil power: 80W, 120W, 150W, 200W (The actual power of the solenoid valve is related to the diameter and pressure parameters, and the larger the diameter and pressure, the greater the power)
Usage pressure: -6.4MPa -+6.4MPa ("-" represents the pressure from the reverse outlet to the inlet, "+" represents the pressure from the forward inlet to the outlet)
Connection method: internal thread, flange, welding
Media used: various media such as water, gas, oil, steam, high-temperature oil, etc
Medium temperature: -200 ℃ -0 ℃, -60 ℃ -+80 ℃, -20 ℃ -+80 ℃, -5 ℃ -+80 ℃, -5 ℃ -120 ℃, 0 ℃ -+200 ℃, 0 ℃ -+600 ℃
Valve body material: stainless steel 304, stainless steel 316, carbon steel
Protection level (optional): Waterproof (IP65), Underwater (IP68), Anti corrosion, Explosion proof (Exd Ⅱ CT5)
Wiring methods: plug type, lead type, junction box
Control mode: normally closed, normally open
Additional features (optional): with manual function, with signal feedback function, with filtering function
Leakage level: Zero leakage
3、 Working principle of bidirectional solenoid valve
Normally closed: The bidirectional solenoid valve is usually in a closed state; When the coil is powered on, the solenoid valve opens, and when it is powered off, the solenoid valve closes. When the solenoid valve is in the open state, the inlet pressure is greater than the outlet pressure, and the medium flows from the inlet end to the outlet end; When the outlet pressure is greater than the inlet pressure, the medium flows from the outlet end to the inlet end. And regardless of whether the medium pressure is greater at the inlet end than at the outlet end, or at the outlet end than at the inlet end, the solenoid valve can cut off the medium after power failure.
Normally open: The bidirectional solenoid valve is usually in the open state; When the coil is powered on, the solenoid valve closes, and when the power is off, the solenoid valve opens. When the solenoid valve is in the open state, the inlet pressure is greater than the outlet pressure, and the medium flows from the inlet end to the outlet end; When the outlet pressure is greater than the inlet pressure, the medium flows from the outlet end to the inlet end. And regardless of whether the medium pressure is greater at the inlet end than at the outlet end or at the outlet end than at the inlet end, the solenoid valve can cut off the medium after being energized.
Note: When the pressure at the outlet end of a regular solenoid valve is higher than that at the inlet end, the medium will continue to flow from the outlet end to the inlet end and cannot be stopped. A bidirectional solenoid valve can prevent this phenomenon from occurring.
Internal structure diagram of bidirectional solenoid valve